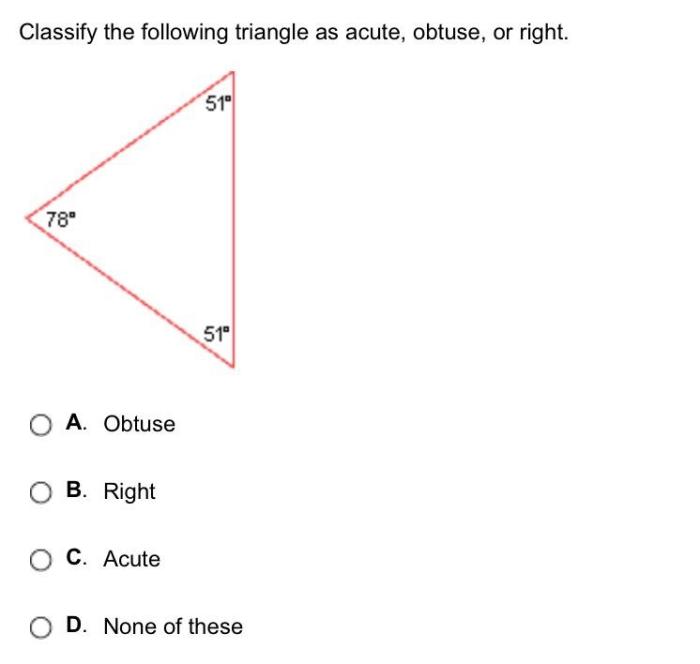
Classify the following triangle as acute obtuse or right apex – Embark on a journey into the realm of triangle classification, where we delve into the intricacies of acute, obtuse, and right triangles. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to confidently identify and categorize triangles based on their angle measurements, empowering you to navigate the world of geometry with precision and understanding.
Through engaging explanations, visual representations, and practical examples, we will unravel the secrets of triangle classification, providing you with a solid foundation in this essential mathematical concept.
Triangle Classification Basics: Classify The Following Triangle As Acute Obtuse Or Right Apex
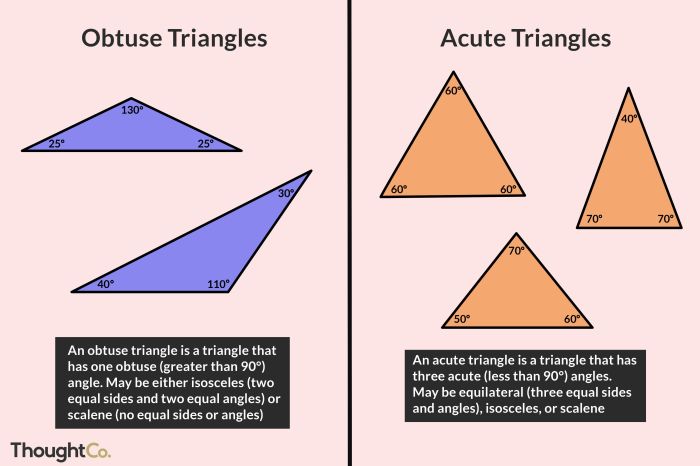
Triangles are classified into three main types based on the measure of their angles: acute, obtuse, and right.
An acute triangle has all three angles measuring less than 90 degrees. An obtuse triangle has one angle greater than 90 degrees. A right triangle has one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees.

Identifying Triangle Types
The following are the characteristics of each triangle type:
- Acute triangle: All angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse triangle: One angle is greater than 90 degrees.
- Right triangle: One angle is exactly 90 degrees.
Here are some examples of each triangle type:
- Acute triangle: 30-60-90 triangle, 45-45-90 triangle
- Obtuse triangle: 30-60-120 triangle, 45-90-135 triangle
- Right triangle: 3-4-5 triangle, 5-12-13 triangle
Measuring Triangle Angles
To measure the angles of a triangle, you will need a protractor.
To use a protractor:
- Place the protractor on one side of the triangle.
- Align the center of the protractor with the vertex of the angle.
- Read the angle measurement on the protractor.
Classifying Triangles Using Angle Measurements
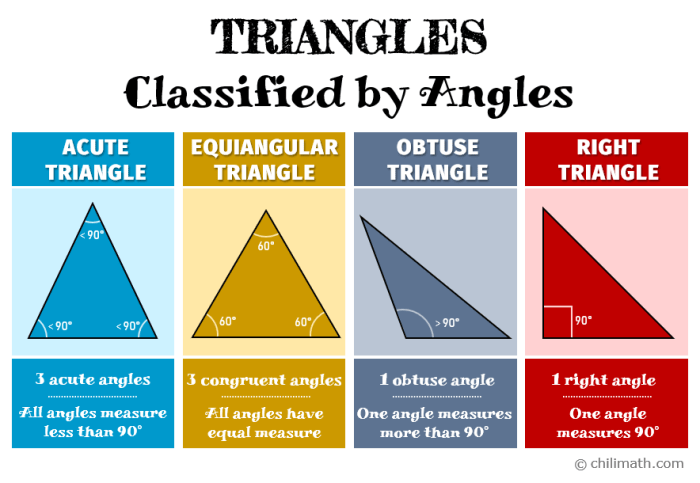
Once you have measured the angles of a triangle, you can classify it using the following criteria:
| Triangle Type | Angle Measurements |
|---|---|
| Acute triangle | All angles are less than 90 degrees. |
| Obtuse triangle | One angle is greater than 90 degrees. |
| Right triangle | One angle is exactly 90 degrees. |
Real-World Applications of Triangle Classification
Triangle classification is used in a variety of real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: To determine the angles of roofs and other structures.
- Engineering: To design bridges, buildings, and other structures that are stable and efficient.
- Navigation: To calculate the distance and direction between two points.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between an acute, obtuse, and right triangle?
Acute triangles have all angles less than 90 degrees, obtuse triangles have one angle greater than 90 degrees, and right triangles have one angle exactly equal to 90 degrees.
How can I measure the angles of a triangle?
You can use a protractor to measure the angles of a triangle by placing the center of the protractor on a vertex and aligning one side of the protractor with one side of the triangle.
What are some real-world applications of triangle classification?
Triangle classification is used in architecture, engineering, surveying, and many other fields to determine the properties and behavior of structures and objects.